AG07 RETENTION AND PURIFICATION
Rainwater retention and purification systems applied to urban design
Aim
Incorporate solutions for rainwater retention, purification and storage both in new urbanizations and in renovations, for streets and other public spaces.
Why?
To mitigate the effects of climate change through design, moderating the rise in the temperature of the planet and the waste of energy and water resources. They bring the following benefits:
► Improvement of the environmental comfort by regulating temperature and humidity.
► Reduction of the heat island effect due to the evaporation of water accumulated in the subsoil.
► Reduction of flooding due to torrential rains by increasing permeable surfaces.
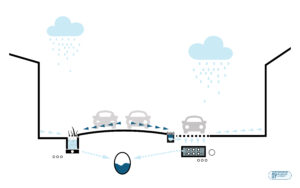
► Decrease of the volumes of runoff and peak flows that end up in the network of collectors and the treatment plant to avoid overloading the sanitation infrastructure.
► Integration of rainwater treatment into the urban landscape.
► Protect water quality by reducing the effects of diffuse pollution.
► Improve the health of urban vegetation.
How?
The solution means to transform current rainwater collection, which seeks the quick evacuation of urban runoff using a system of impermeable surfaces and gutters connected to the sewers, into a network that retains and infiltrates the water from urban runoff.
They are suitable for those places where, due to the conditions of the land (low permeability, contamination of the land, existing underground infrastructures or installations, heritage remains, risk for the foundations of buildings, etc.), it is not appropriate to infiltrate water directly into the subsoil.
The water stored favours the growth of vegetation or a combination with other storage elements and can be used for non-consumptive uses.
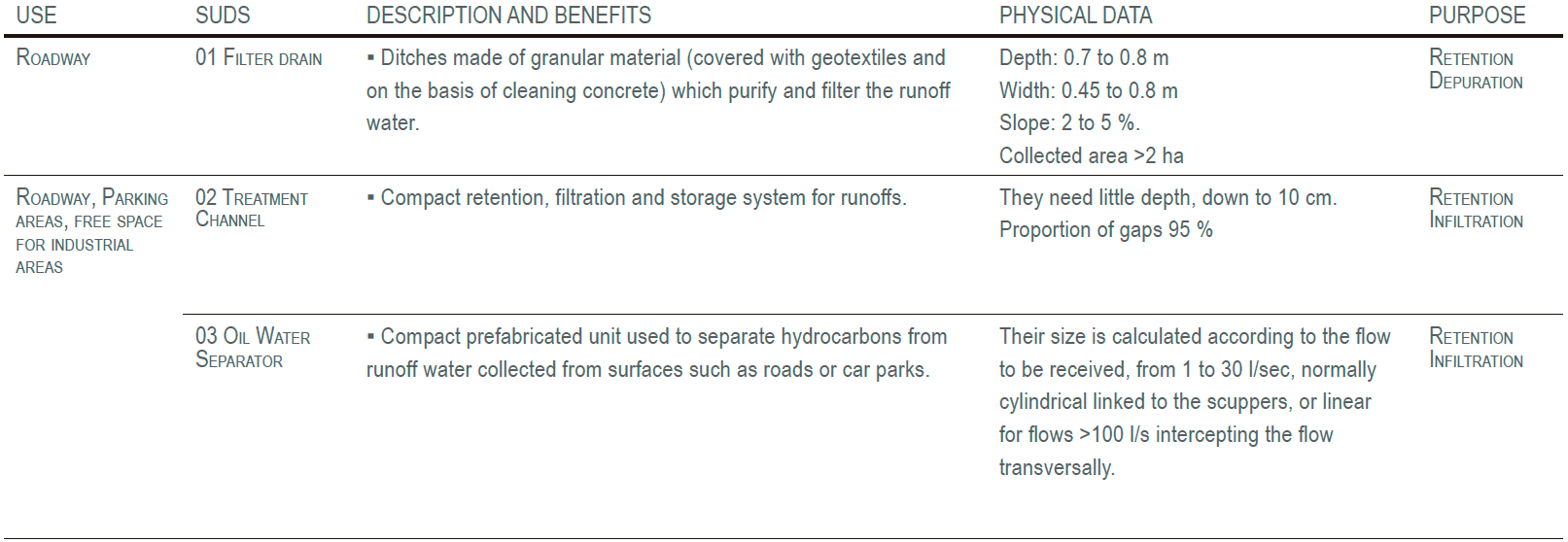 Drainage diagram: retention filtration in the street with overflow channel to the sewage system
Drainage diagram: retention filtration in the street with overflow channel to the sewage system
 |
 |
 |
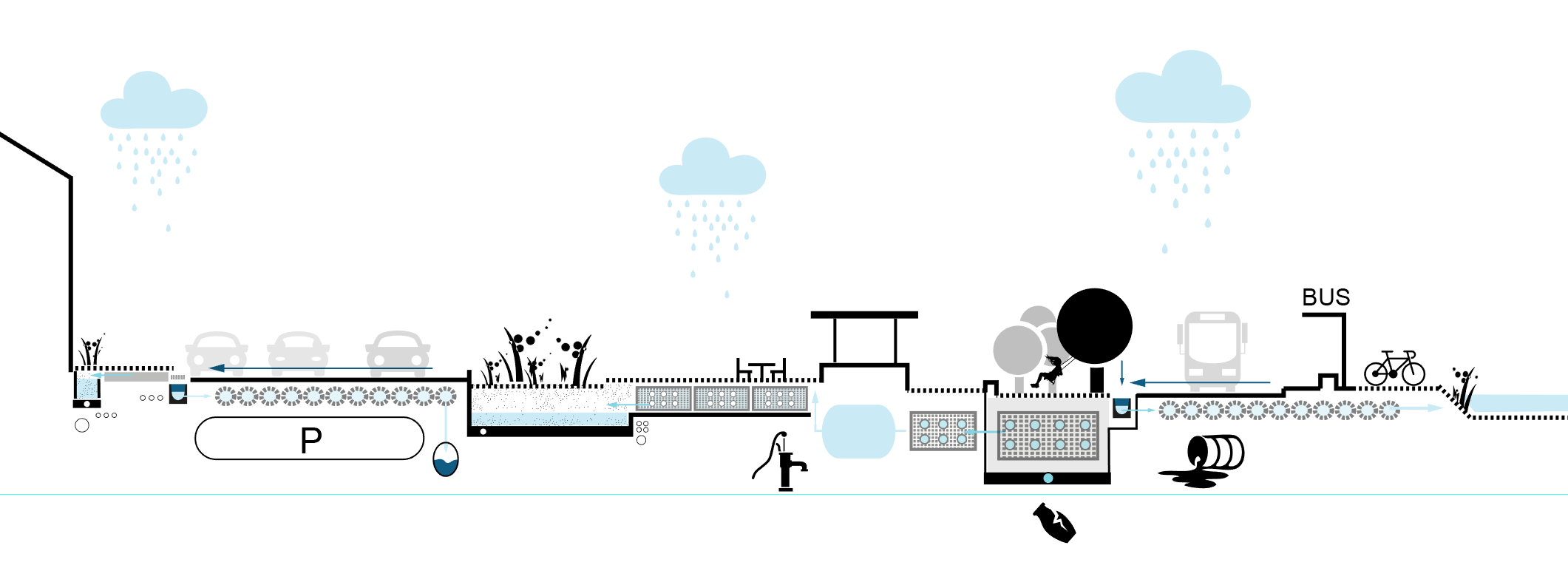
Wanda•Atletico Metropolitano Arena Urbanization Project, roads and parking
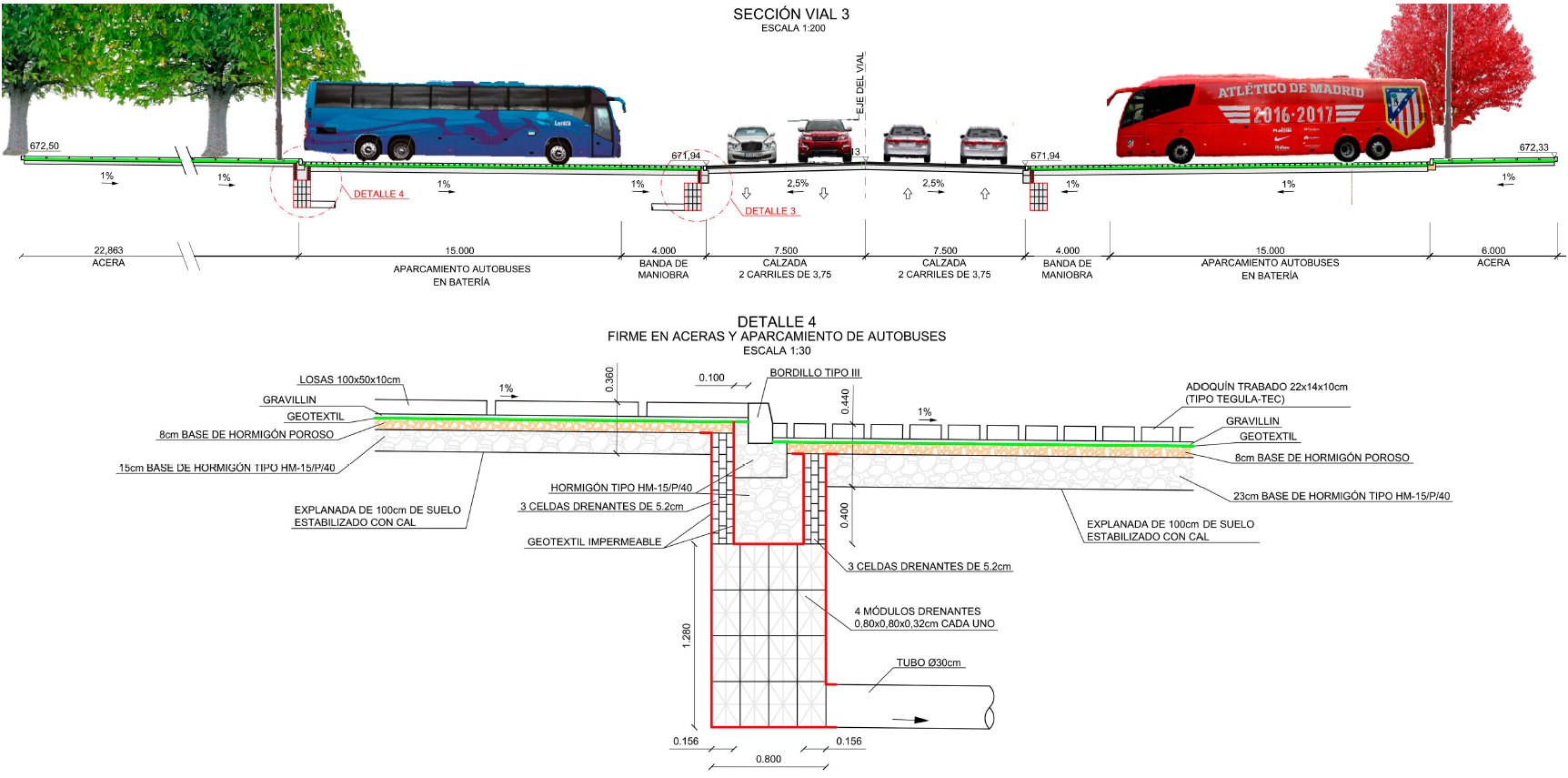
Street scale intervention
ISSUES AFFECTED
SUITABLE FOR COMBINING WITH OTHER SOLUTIONS
MEASURE ELEMENTS
Indicator
Reduction of energy consumption by rainwater infiltration or capture (∆CE)
Secondary indicator
Percentage of retention areas in free space (roads, car parks)
Unit
(I1) m2 of retention area → ∆CE
(I2) %
Minimum goal
>60%
Desirable goal
>95%
Método de medición / Formula
(I1) ΔCE = [A x B]
A: m3 (retentioned and depurated)
B: Energy consumption in MWh per m3 treated at the WWTP
(I2) % = [A / B]
A: m2 of permeable pavements
B: total area
PLANNING LEVEL
Urban planning
Public space restoration plans (parking spaces, roads)
Mobility plans
AGENTS INVOLVED
Local government technicians
Provincial / General administration technicians
Natural spaces or water resources agents
Possible actions promoted by the administration
– In new developments or restoration in roads or public space, incorporate this prefabricated elements that are easy to install.
– Minimize the loss of drainage capacity through good maintenance
What should we consider for its implementation?
– The presence of underground services, such as fibre optics, electrical and telephone cables, or drainage pipes.
– Maintenance of the public space.
– presence of archaeological or environmental elements in the subsoil.